React useEffect 前世今生
在使用 useEffect 的时候,我们可能会产生以下的疑问:
useEffect一定要写在函数顶层吗?useLayoutEffect和useEffect哪个先执行,destroy呢?
相信读完本文后,你能够对这些问题有更深入的理解。
为什么有 React Hook
- class 组件书写复杂繁重,逻辑不容易复用
- 函数组件无法存储状态
- 函数组件无法拥有生命周期函数,因为每次都会重新调用(但对于 class 组件则不同,实际运行时是一个实例)
useEffect 含义
effect 翻译过来就是副作用。实际上 useEffect 就是一个函数
useEffect 用法
useEffect(fn, [deps])
其中, fn 是副作用引发的回调函数,还可以返回一个函数(会在组件卸载或者下一次更新前被调用)。deps 是依赖数组,需要开发者手动维护依赖数组。
源码表现
源码流程图
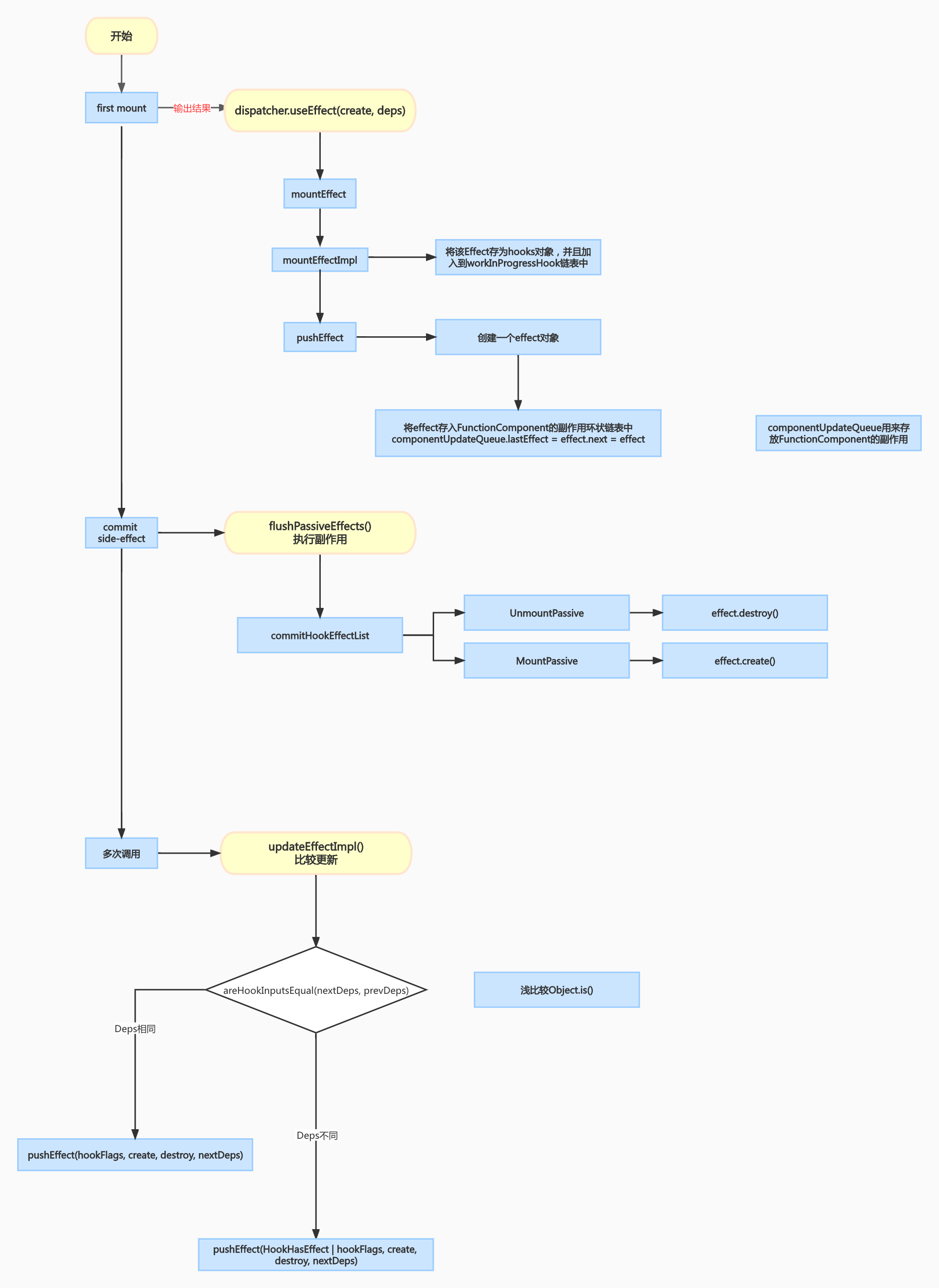
初始化时
在源码实现上也是一个函数,上源码:
export function useEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
inputs: Array<mixed> | void | null
) {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useEffect(create, inputs);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
dispatcher 是什么?
来看下 dispatcher 的结构:
export type Dispatcher = {
useState<S>(initialState: (() => S) | S): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>],
useReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: (I) => S
): [S, Dispatch<A>],
useEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null
): void,
useLayoutEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null
): void,
...
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
可以看到 dispatcher 维护了 hook 的入口.
在 React 源码中,对应分了两种 dispatcher,比如 HooksDispatcherOnMount 、比如 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate(实际还有一种专门给错误提示用的:ContextOnlyDispatcher)。
虽然我们代码中仅仅是写了 useEffect 一份代码,但是在源码中,实际上分了 mount 和 update 两种情形,
所以,在函数组件初始化的时候,dispatcher 为 HooksDispatcherOnMount,此时会调用以下函数
useEffect: function (create, deps) {
currentHookNameInDev = 'useEffect';
mountHookTypesDev();
checkDepsAreArrayDev(deps);
return mountEffect(create, deps);
}
2
3
4
5
6
mountEffect 原理
那么 mountEffect 又是什么函数呢
// https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/main/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js
function mountEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null
): void {
return mountEffectImpl(
UpdateEffect | PassiveEffect,
HookPassive,
create,
deps
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
下面会涉及到几个常量的概念,比如 fiberEffectTag、 HookFlags
fiberEffectTag
fiberEffectTag 是 fiber 定义的副作用的 tag,也就是常量,但这里很有意思的是,用的是二进制
// Don't change these two values. They're used by React Dev Tools.
export const NoFlags = /* */ 0b000000000000000000;
export const PerformedWork = /* */ 0b000000000000000001;
// You can change the rest (and add more).
export const Placement = /* */ 0b000000000000000010;
export const Update = /* */ 0b000000000000000100;
export const PlacementAndUpdate = /* */ 0b000000000000000110;
export const Deletion = /* */ 0b000000000000001000;
export const ContentReset = /* */ 0b000000000000010000;
export const Callback = /* */ 0b000000000000100000;
export const DidCapture = /* */ 0b000000000001000000;
export const Ref = /* */ 0b000000000010000000;
export const Snapshot = /* */ 0b000000000100000000;
export const Passive = /* */ 0b000000001000000000;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
为什么用二进制呢,我想有以下原因:
- 在一次渲染任务中可能会多次使用到这里的值,那么二进制的位运算就能够拉升运行时的性能。
- 同时如果我要表示多个副作用,比如我副作用包含 Placement 和 Update,那么 PlacementAndUpdate = Placement | Update 。按位运算还是很方便的。
HookFlags
export type HookFlags = number;
export const NoFlags = /* */ 0b000;
// Represents whether effect should fire.
export const HasEffect = /* */ 0b001; // 有副作用
// Represents the phase in which the effect (not the clean-up) fires.
export const Layout = /* */ 0b010;
export const Passive = /* */ 0b100;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
下面我们来看下 mountEffectImpl:
function mountEffectImpl(fiberEffectTag, hookEffectTag, create, deps) {
var hook = mountWorkInProgressHook(); // 返回一个链表
var nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.effectTag |= fiberEffectTag;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HasEffect | hookEffectTag,
create,
undefined,
nextDeps
);
}
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
pushEffect 原理:
function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
const effect: Effect = {
tag,
create,
destroy,
deps,
next: (null: any),
};
let componentUpdateQueue: null | FunctionComponentUpdateQueue =
(currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue: any);
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) {
componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue();
currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = (componentUpdateQueue: any);
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
if (lastEffect === null) {
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
lastEffect.next = effect;
effect.next = firstEffect;
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
}
}
return effect;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
pushEffect 的作用就是创建一个 Effect 对象,并把这个对象添加到 componentUpdateQueue 中,而在初始化的时候,又把 componentUpdateQueue 添加到了 currentlyRenderingFiber 中。通过这样把副作用和 fiber 产生了关联。
更新时
在函数更新的时候,会调用以下函数:
function updateEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null
): void {
return updateEffectImpl(
UpdateEffect | PassiveEffect,
UnmountPassive | MountPassive,
create,
deps
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
可以看到,这个函数和 mountEffectImpl 入参是一样的。
function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps): void {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
let destroy = undefined;
if (currentHook !== null) {
const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps); // 注意,这里没有副作用,也需要pushEffect。保证Hook顺序相同
return;
}
}
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags, // 这里代表了有副作用
create,
destroy,
nextDeps
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
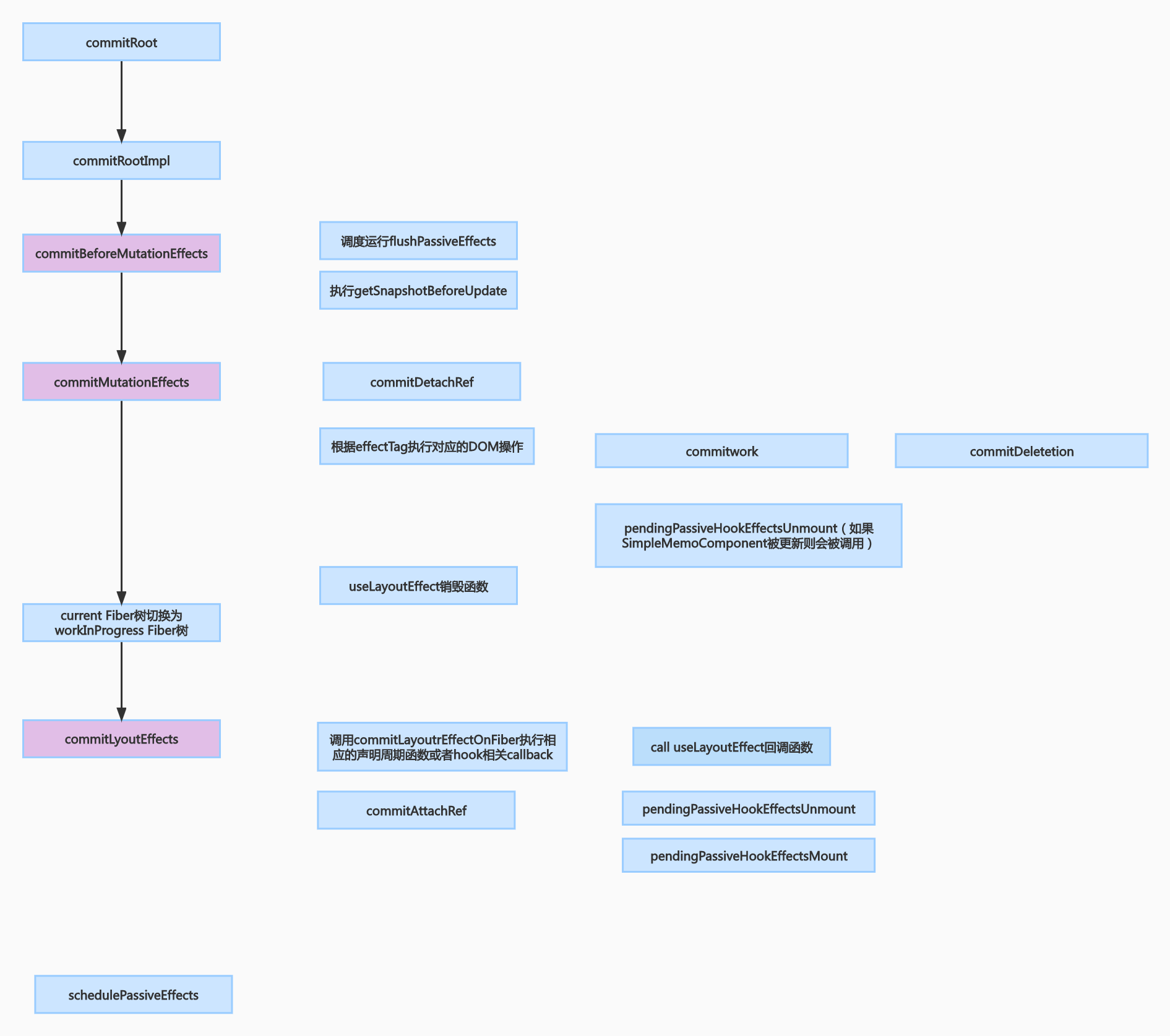
commit 阶段调用时机
useEffect 问答
useEffect 依赖项对比是浅比较吗
在更新时会调用到 updateEffectImpl,具体可以看 updateEffectImpl 的实现,其中有一段 deps 的对比如下:
function areHookInputsEqual(
nextDeps: Array<mixed>,
prevDeps: Array<mixed> | null
) {
if (prevDeps === null) {
return false;
}
for (let i = 0; i < prevDeps.length && i < nextDeps.length; i++) {
if (is(nextDeps[i], prevDeps[i])) {
continue;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
可以看到对比的逻辑是依次取出依赖函数,然后进行 is 比较,Object.is 的实现是一个浅对比,也就是如果你直接修改原对象的一个 key 对应的 value 值,就会导致这里并不能触发调用,也就不会产生副作用。那么对应的解决方案是你可以使用不可变的方式,比如对象解构 {...deps}
useEffect 与 useLayoutEffect 区别
大家可能都有个朦胧的概念是,两个副作用的回调的被调用时机是在 DOM 树被更新之后。具体执行时机还得看源码,由上一章节可以看到 useEffect/useLayoutEffect 都会在 commit 阶段被执行。
在 commit 阶段,分为 3 大循环:
commitBeforeMutationEffects: 调度运行 flushPassiveEffects。这个调度指的是以普通优先级,被推入了 commit 阶段后 的 task 中,在浏览器重排/绘制后,依次调用这些回调(异步)。 commitMutationEffects: 执行 DOM 操作。这里会附带一些组件的卸载,所以 useLayoutEffect 的销毁函数会在这里被调用。 commitLayoutEffect: DOM 树已经更新完毕了,此时会先调用 useLayoutEffect 的回调(同步),再进行 flushPassiveEffects 里面的这些 task
useEffect 一定要写在函数顶层吗?
是的。因为所有的 hook 都会按顺序依次维护在 hook 链表中。假如你的某个 hook 不写在顶层,例如某个 hook 加了 if 判断,那么更新的时候,链表顺序则会对应不上初始化/上一次更新的 hook 的顺序了。
useEffect 可以写 async 吗
不能, useEffect 第一个参数的 function 需要返回 undefined 或者另一个 funciton
如果有多个逻辑,使用多个 useEffect 还是一个 useEffect
回答是不同逻辑,应该分开使用不同的 useEffect。componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect 也会依次存入多个副作用的回调。
useEffect 未来发展
useEffect 依赖项是必填的吗
In the future, the second argument might get added automatically by a build-time transformation.
For more detail, you could wath the share: React Forget:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lGEMwh32soc&t=2s
2
总结
翻看 useEffect 的源码,会发现 Hooks 的知识其实与 fiber、渲染的流程(render/commit 阶段)息息相关,也是借助了 fiber,React 才能够在函数中实现了 Hooks 的状态的存储。所以如果想真正了解透彻 hook 的涉及,就需要深入理解 fiber 的设计以及 React 渲染流程的原理。所以,我们接下来的源码解析将会继续学习 fiber 的设计以及 React 渲染流程,敬请期待!
参考文章
https://overreacted.io/zh-hans/a-complete-guide-to-useeffect/
本文的作者是 Luo,来自 海码团 团队。